Mangroves are crucial for biodiversity, climate change mitigation, and coastal protection but face threats from climate change and human activities. Traditional monitoring methods fall short in accurately capturing their complex features.
The integration of advanced machine learning algorithms with multisource remote sensing data offers a promising solution. Based on these challenges, it is essential to conduct in-depth research to develop more precise and effective techniques for mangrove species classification, which can significantly enhance conservation and restoration efforts.
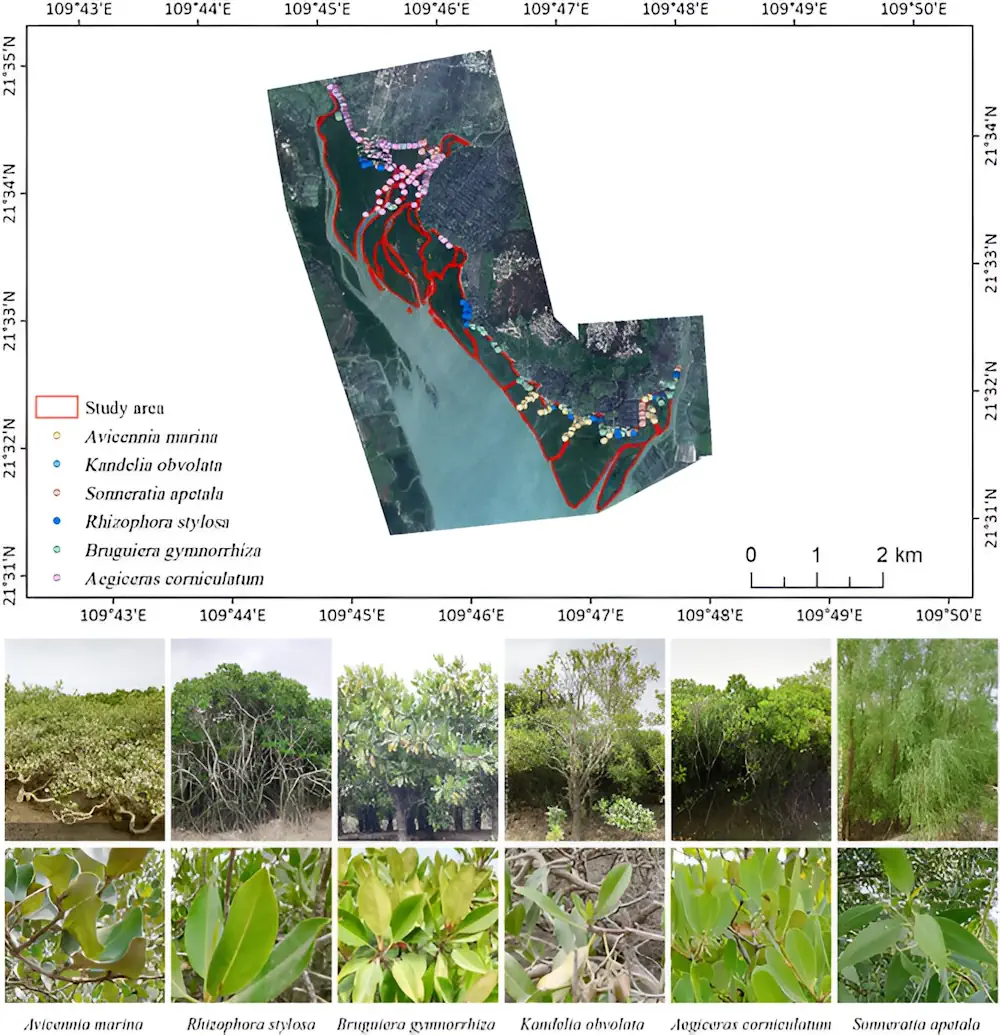
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a novel framework for mangrove species classification using an XGBoost ensemble learning algorithm, as published in the Journal of Remote Sensing, on 6 Jun 2024. The study, which combines multisource remote sensing data, offers a significant leap in the precision of mangrove species mapping.
The study examined the Zhanjiang Mangrove National Nature Reserve in China, using data from WorldView-2, OrbitaHyperSpectral, and ALOS-2 satellites. Researchers extracted 151 remote sensing features and designed 18 classification schemes to analyze the data. By combining these features with the XGBoost algorithm and recursive feature elimination, they achieved an impressive classification accuracy of 94.02%.
The integration of multispectral, hyperspectral, and synthetic aperture radar data proved highly effective in distinguishing six different mangrove species. This approach demonstrated that the combined data sources significantly improved classification results compared to single-source data.